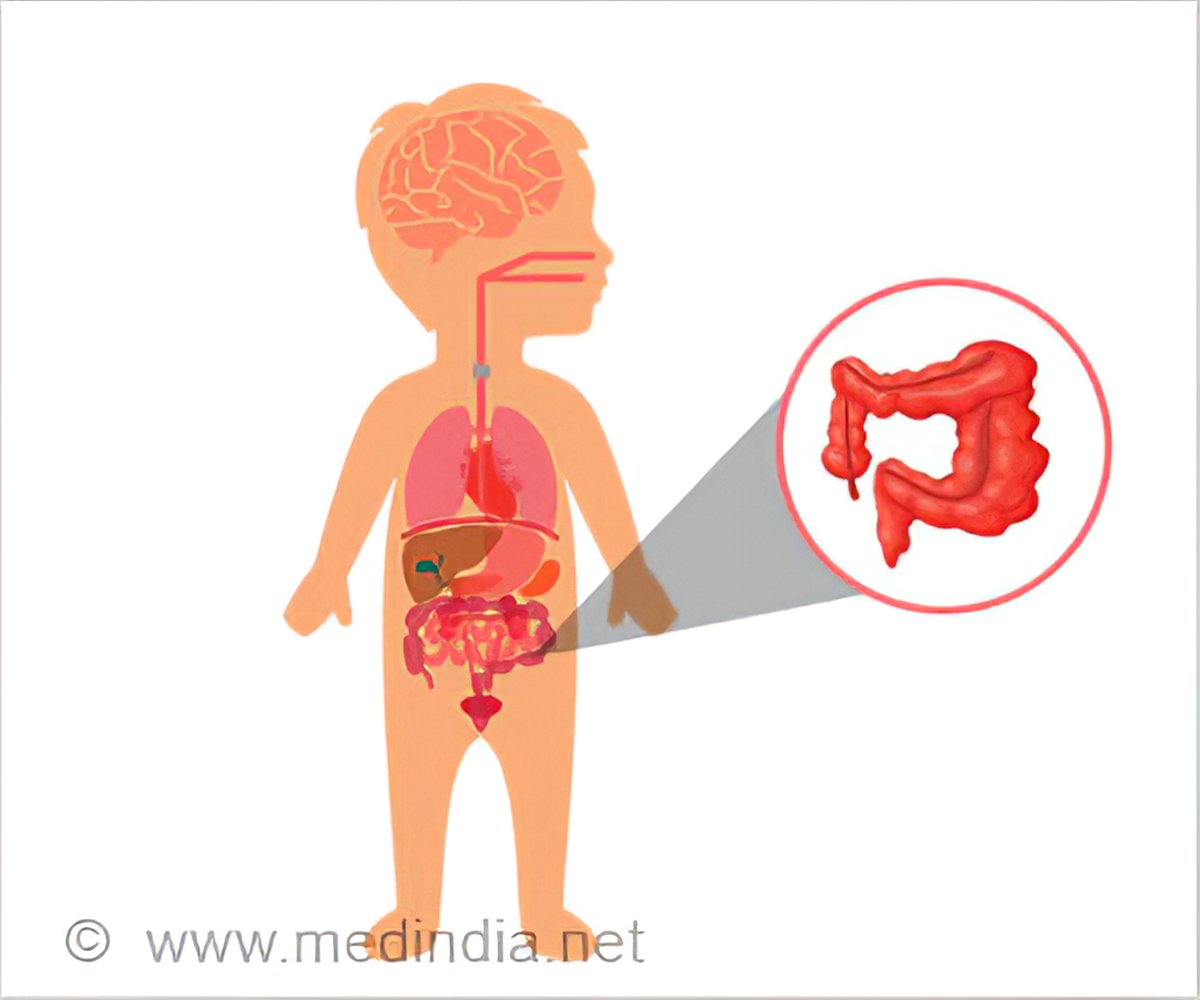
pseudomembranous colitis in babies
Pseudomembranous colitis PMC is inflammation in your colon that happens when theres too much of certain bacteria in your system. Pseudomembranous colitis is inflammation swelling irritation of the large intestine.

C Diff Infection Causes Symptoms 8 Natural Treatments Dr Axe
Pseudomembranous colitis in children.

. Difficile is often related to a recent. However it is becoming more common in people who take antibiotics and are not in a hospital. Difficile infection in any child.
Necrotizing enterocolitis a condition pathologically distinct from pseudomembranous colitis was also present. Pseudomembranous colitis severe inflammation of the inner lining of the bowel from C. Food and Drug Administration FDA has approved the use of human monoclonal antibody bezlotoxumab to reduce the risk of recurrence of C.
Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children. There are limited descriptions of pseudomembranous colitis in children. 8586 Infants and young children rarely are affected.
It is necessary to consider the C. Oral metronidazole 400mg 10mgkg 8 hourly for 10 days can be given IV Severe. What is pseudomembranous colitis.
The ages ranged from 4 years to 17 years. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC occurs rarely in children but its incidences are increasing due to frequent antibiotic use. Pseudomembranous SOO-doe-mem-bruh-nus colitis also called antibiotic-associated colitis or C.
Pseudomembranous colitis PMC occurs rarely in children but its incidences are increasing due to frequent antibiotic use. Certain antibiotics like penicillin clindamycin Cleocin the cephalosporins and the. PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization.
Pseudomembranous SOO-doe-mem-bruh-nus colitis also called antibiotic-associated colitis or C. Full text Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Youll receive healthy cleaned stool in a capsule nasogastrically or inserted into your colon.
Approach to diarrhea in children in resource-rich countriessystemic toxicity. Bolton RP Thomas DF. This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children.
Pseudomembranous colitis is an infection of the colon due to overgrowth of a bad bacteria clostridium difficele. It causes inflammation of the lining. Using antibiotics can cause the bacterium Clostridium difficile C.
Two cases of ischemic necrosis of the sigmoid colon associated with pseudomembranous colitis due to Schistosoma mansoni in children have been reported. Get a printable copy PDF file of the complete article 295K or click on a page image below to browse page by page. Pseudomembranous colitis in children and adults.
Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. Stool assays showed specimens from all ten patients yielded a cytopathic toxin which was neutralized by Clostridium sordellii antitoxin. Jayakar AV Desai AG Dalal NJ Shah SC Narayan K.
There are limited descriptions of pseudomembranous colitis in children. Ampicillin amoxicillin the second- and third-generation cephalosporins and clindamycin. Use of medicines that weaken the immune system such as chemotherapy medicines.
The diagnosis of pseudomembranous was established clinically and was confirmed by colonoscopy and the presence of Clostridium difficile toxin A in the stools. Clostridial toxin in faeces of healthy infants. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References.
This overgrowth of C. Identification of Clostridium difficile as the major pathogen has led to a rational successful approach to therapy and has widened the spectrum of associated disease. Pseudomembranous colitis is uncommon in children and rare in infants.
Oral vancomycin 125mg 3mgkg 6 hourly for 10 days IV not effective Disposition will depend on the patient co. Antibiotic-associated colitis is a rare complication of antimicrobial therapy in children. It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile.
Viscidi RP Bartlett JG. Ten cases of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children are reviewed. FMT is used to treat recurrent pseudomembranous colitis.
Difficile colitis is inflammation of the colon associated with an overgrowth of the bacterium Clostridioides difficile formerly Clostridium difficile often called C. Diff to grow and infect the lining of the intestine which produces the inflammation. This diagnosis should be suspected in any child with significant diarrhea during or after a course of antimicrobial therapy especially if the diarrhea persists.
It is most often seen in people who are in the hospital. Ampicillin penicillin and clindamycin are the drugs most frequently reported to cause pseudomembranous colitis in pediatric patients. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC is commonly associated with hospitalization and prior antibiotic exposure.
Pseudomembranous colitis in children INTRODUCTION. Pseudomembranous colitis remains a potentially lethal complication of antibiotic usage. Ten cases of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children are reviewed.
Difficile infection is uncommon in children. The pseudomembranous colitis developed 12 days after the last dose of ampicillin was given to the baby. Stool assays showed specimens from all ten patients yielded a cytopathic toxin which was neutralized by.
The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. General Surgery 39 years experience. Pseudomembranous colitis in children.
The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. A 32-year-old member asked. The patients developed acute abdomen and underwent laparotomy that showed necrosis of the bowel.
Early surgical referral may require colectomy. The ages ranged from 4 years to 17 years. In many cases it occurs after taking antibiotics.
The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. Rietra PJ Slaterus KW Zanen HC Meuwissen SG. Toxic megacolon can occur as a complication of.

Clostridium Difficile Infection What You Need To Know Consultant360
Enterocolitis Types Symptoms Treatment And Diet

Clostridium Difficile Pha Infection Control
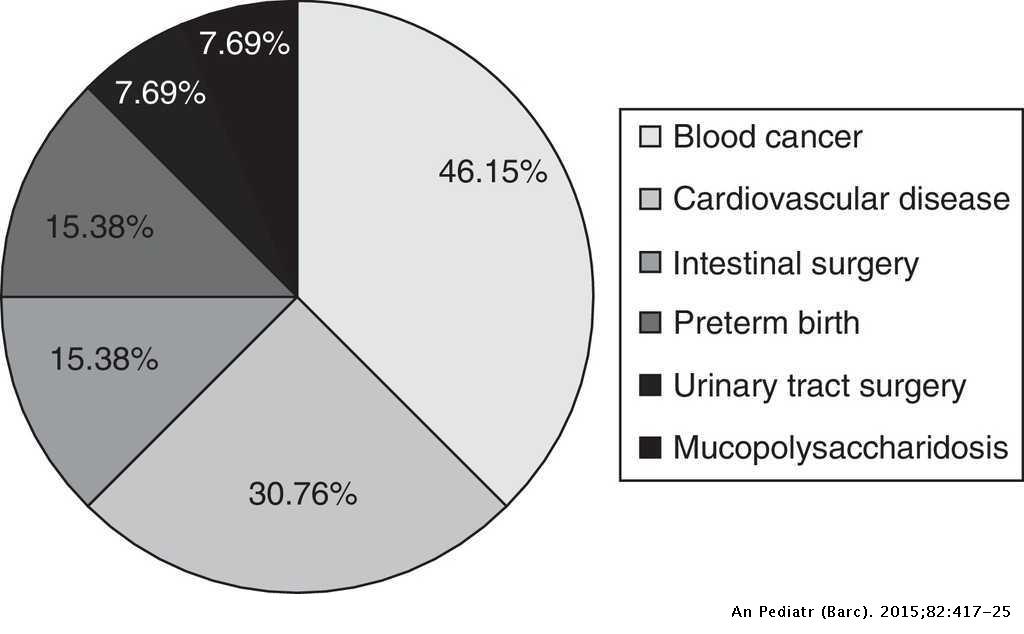
Clostridium Difficile Isolation In Children Hospitalized With Diarrhoea Anales De Pediatria
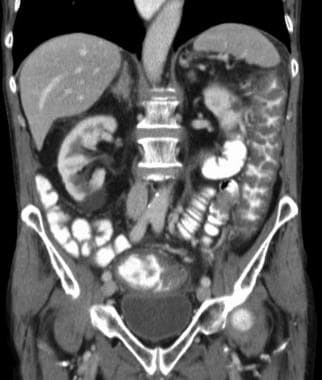
Clostridioides Clostridium Difficile Colitis Workup Approach Considerations Stool Examination And Stool Assays Endoscopy

What Is Enterocolitis Causes Symptoms Treatment Diet

Clostridium Difficile Associated Diarrhea American Family Physician

Infections Caused By C Difficile In Children Explained Wonderbaba
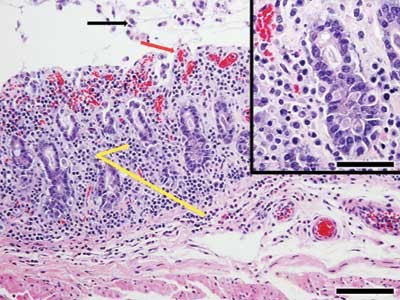
Diagnosis Clostridium Difficile Induced Typhlitis And Colitis Lab Animal

Lactobacillus Reuteri Dsm 17938 In The Prevention Of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea In Children A Randomized Clinical Trial Clinical Microbiology And Infection

Baby With White Plaques On The Tongue Consultant360

Clostridium Difficile C Diff Infectious Dis Medbullets Step 2 3
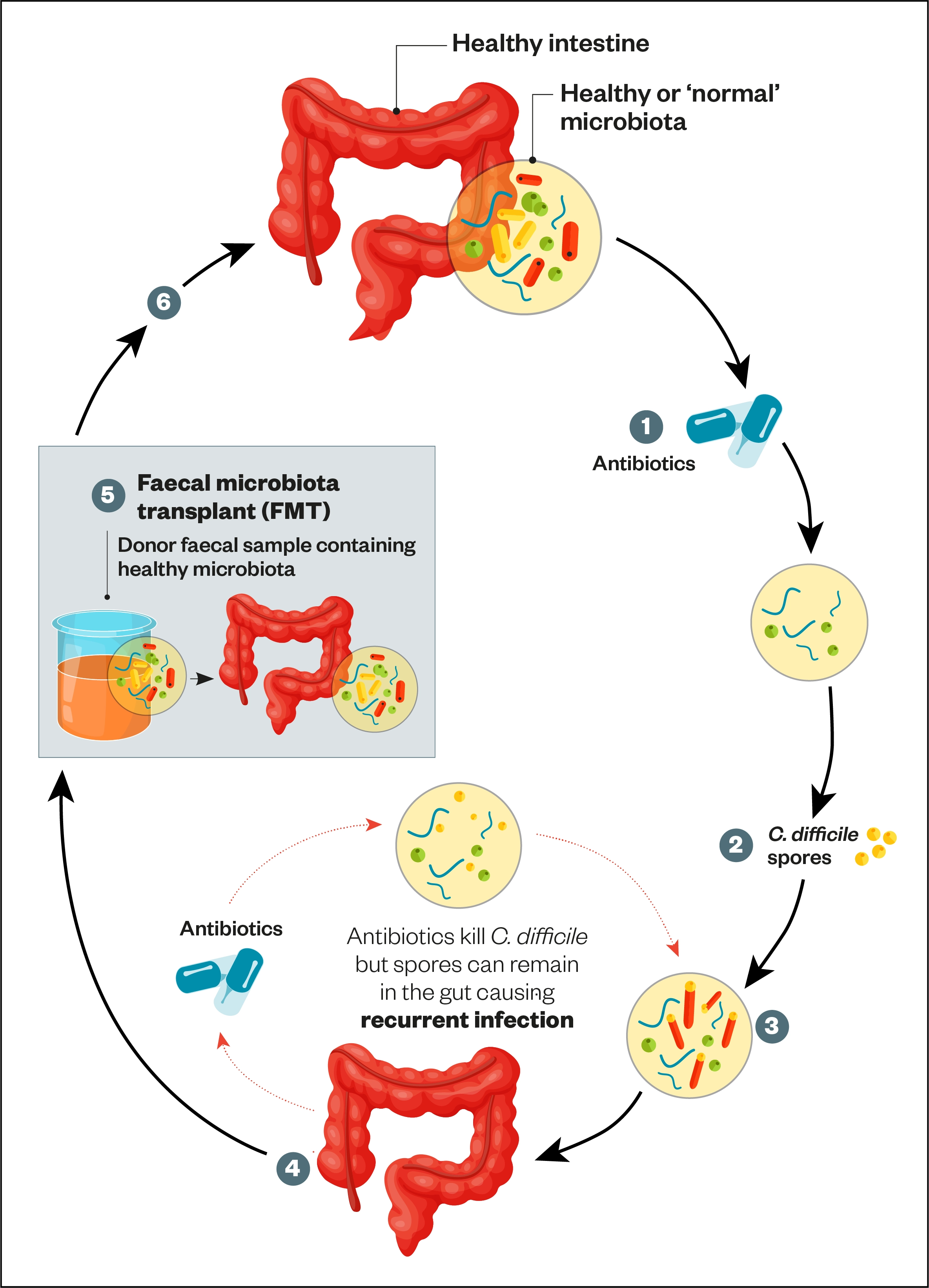
Clostridioides Difficile Infection Management The Pharmaceutical Journal

References In Necrotizing Enterocolitis Continuing Education In Anaesthesia Critical Care And Pain

Welcome To The Infant Botulism Treatment And Prevention Program
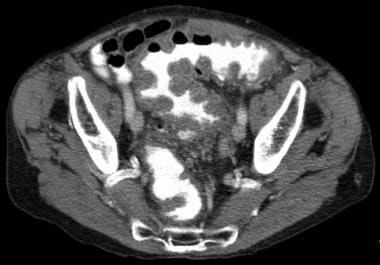
Clostridioides Clostridium Difficile Colitis Workup Approach Considerations Stool Examination And Stool Assays Endoscopy